Pelosi to Bishops: Use Pulpit to Promote Immigration Reform
The Ch. 17 Sec. 3 Quiz is on Wednesday. Be sure to consult the Chapter 17 Section 3 Quiz Study Prep Page.
Chapter 18: Nationalism Around the World, 1919–1939
Section 4 Nationalism in Latin America
The Latin American Economy
Role of the United States
Impact of the Great Depression
The Move to Authoritarianism
Argentina
Brazil
Mexico
The Constitution of 1917 addressed three major issues: land, religion, and labor. The constitution strengthened government control over the economy. It permitted the breakup of large estates, placed restrictions on foreigners owning land, and allowed nationalization, or government takeover, of natural resources. Church land was made “the property of the nation.” The constitution set a minimum wage and protected workers’ right to strike.
Although the constitution gave suffrage only to men, it did give women some rights. Women doing the same job as men were entitled to the same pay. In response to women activists, Carranza also passed laws allowing married women to draw up contracts, take part in legal suits, and have equal authority with men in spending family funds.
Fighting continued on a smaller scale throughout the 1920s, including Carranza’s overthrow in 1920. In 1929, the government organized what later became the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI). The PRI managed to accommodate many groups in Mexican society, including business and military leaders, peasants, and workers. The PRI did this by adopting some of the goals of these groups, while keeping real power in its own hands. It suppressed opposition and dissent. Using all of these tactics, the PRI brought stability to Mexico and over time carried out many desired reforms. The PRI dominated Mexican politics from the 1930s until the free election of 2000.
The Institutional Revolutionary Party PRI and Vicente Fox, 1:32
At first, the Constitution of 1917 was just a set of goals to be achieved in the future. But in the 1920s and 1930s, as the government finally restored order, it began to carry out reforms.
In the 1920s, the government helped some Indian communities regain lands that had been taken from them. In the 1930s, under President Lázaro Cárdenas, millions of acres of land were redistributed to peasants under a communal land program. The government supported labor unions and launched a massive effort to combat illiteracy. Schools and libraries were set up. Dedicated teachers, often young women, worked for low pay. While they taught basic skills, they spread ideas of nationalism that began to bridge the gulf between the regions and the central government. As the revolutionary era ended, Mexico became the first Latin American nation to pursue real social and economic reforms for the majority of its people.
The government also took a strong role in directing the economy. In 1938, labor disputes broke out between Mexican workers and the management of some foreign-owned petroleum companies. In response, President Cárdenas decreed that the Mexican government would nationalize Mexico’s oil resources. American and British oil companies resisted Cárdenas’s decision, but eventually accepted compensation for their losses. Mexicans felt that they had at last gained economic independence from foreign influence.
Reading Check
Examining
Culture in Latin America
By the 1920s, Latin American writers, artists, and thinkers began to reject European influences in culture as well. Instead, they took pride in their own culture, with its blend of Western and native traditions.
In Mexico, cultural nationalism, or pride in one’s own culture, was reflected in the revival of mural painting, a major art form of the Aztecs and Maya. In the 1920s and 1930s, Diego Rivera, José Clemente Orozco (oh rohs koh), David Alfaro Siqueiros (see keh rohs), and other muralists created magnificent works. On the walls of public buildings, they portrayed the struggles of the Mexican people for liberty. The murals have been a great source of national pride ever since.
Jose Clemente Orozco Murals in Guadalajara, Mexico, 2:58
Murals painted by Jose Clemente Orozco in Guadalajara, Mexico.
David Alfaro Siqueiros, 6:07
Diego Rivera, 4:50
Reading Check
Examining
How did Diego Rivera use his artistic talent as a political tool?
Preview
Chapter 19 World War II 1939-1945
Chapter 19: World War II, 1939–1945
The German and Japanese occupations of neighboring countries led to a brutal war that took millions of lives. Both countries were defeated, but not before the Nazis had killed millions of people in pursuit of Aryan domination of Europe.
Section 1 Paths to War
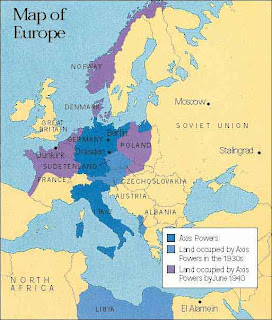
Aggressive moves by Germany and Japan set the stage for World War II. Adolf Hitler began a massive military buildup and instituted a draft in violation of the Treaty of Versailles. The German annexation of Austria alarmed France but did not shake Great Britain's policy of appeasement. Mussolini became a German ally. Appeasement of Germany peaked at a conference in Munich where Hitler claimed he sought only one final territory, the Czech Sudetenland. This soon proved false. When Hitler signed a nonaggression pact with Stalin and invaded Poland, Britain and France declared war on Germany. Japanese expansion into Manchuria and northern China brought condemnation from the League of Nations. While still at war with China, Japan launched a surprise attack on U.S. and European colonies in Southeast Asia.
Section 2 The Course of World War II
German forces swept through northern Europe early in the war and set up the Vichy government in France. German air attacks on Great Britain resulted in fierce British retaliation. In the east, harsh weather and a resolute Soviet Union defeated an invading German army. The Japanese conquered the Pacific but miscalculated when they attacked the U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor. The United States surprised Japan by abandoning its neutrality and entering the war to retake the Pacific. By the end of 1943, the tide had turned against Germany, Italy, and Japan. After the invasion of Normandy, the Allies liberated Paris and defeated Germany. U.S. President Harry Truman, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill, and Soviet Premier Josef Stalin met at Potsdam, Germany, to plan the post-war world. The war in Asia continued until the United States dropped atomic bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, causing massive casualties and bringing Japan's surrender.
Section 3 The New Order and the Holocaust
To further their war effort and Hitler's plans for Aryan expansion, the Nazis forced millions of people to resettle as forced laborers. No aspect of the Nazi New Order was more terrifying than the deliberate attempt to exterminate the Jews. As part of the Nazis' Final Solution, Jews were locked into cramped, unsanitary ghettos or forced to dig their own mass graves before being killed. When this proved too slow for the Nazis, they transported Europe's Jews to death camps where they were worked to death or sent to die in gas chambers. The Nazis killed between five and six million Jews and nine to ten million non-Jews. In Asia, Japan showed little respect for the conquered peoples in its effort to secure industrial markets and raw materials. Japanese treatment of prisoners of war was equally harsh. Japan professed a commitment to ending Western colonialism, but the brutality of the Japanese convinced many Asians to resist Japanese occupation.
Section 4 The Home Front and the Aftermath of the War
World War II reached almost every area of the world, and mobilization for war brought widespread suffering and even starvation. The war caused 20 million civilian deaths. The United States, which did not fight the war on its own territory, sent its forces to fight and produced much of the military equipment for the Allies. Segregation in the U.S. military led African Americans to demand civil rights. Racism and suspicion led to the war-time detention of more than 100,000 Japanese Americans. The bombing of cities by the Allied and Axis powers cost thousands of lives, but probably did nothing to weaken the morale of either side. After the war, ideological conflict between the West and the Soviet Union resulted in the Cold War. The Cold War centered around the status of Soviet-dominated Eastern Europe.
Chapter 19 World War II 1939-1945
Section 1 Paths to War
Aggressive moves by Germany and Japan set the stage for World War II. Adolf Hitler began a massive military buildup and instituted a draft in violation of the Treaty of Versailles. The German annexation of Austria alarmed France but did not shake Great Britain's policy of appeasement. Mussolini became a German ally. Appeasement of Germany peaked at a conference in Munich where Hitler claimed he sought only one final territory, the Czech Sudetenland. This soon proved false. When Hitler signed a nonaggression pact with Stalin and invaded Poland, Britain and France declared war on Germany. Japanese expansion into Manchuria and northern China brought condemnation from the League of Nations. While still at war with China, Japan launched a surprise attack on U.S. and European colonies in Southeast Asia.
Note Taking
Reading and Listening Skill: Recognize Sequence
As you read and listen, keep track of the sequence of events that led to the outbreak of World War II by completing a table like the one below.
Reading Skill: Recognize Sequence
Complete this timetable of German aggression as you read.
The German Path to War
Hitler pursued his goal of bringing all German-speaking people into the Third Reich. He also took steps to gain “living space” for Germans in Eastern Europe. Hitler, who believed in the superiority of the German people, or “Aryan race,” thought that Germany had a right to conquer the inferior Slavs to the east. “Nature is cruel,” he claimed, “therefore we, too, may be cruel. . . .I have the right to remove millions of an inferior race that breeds like vermin.”
Hitler on the History of the Aryan Race (Mein Kampf in English), 3:10
Throughout the 1930s, challenges to peace followed a pattern. Dictators took aggressive action but met only verbal protests and pleas for peace from the democracies. Mussolini, Hitler, and the leaders of Japan viewed that desire for peace as weakness and responded with new acts of aggression. With hindsight, we can see the shortcomings of the democracies’ policies. These policies, however, were the product of long and careful deliberation. At the time, some people believed they would work.
The First Steps
Hitler, too, had tested the will of the Western democracies and found it weak. First, he built up the German military in defiance of the treaty that had ended World War I. Then, in 1936, he sent troops into the “demilitarized” Rhineland bordering France—another treaty violation.
March 1936 Rhineland remilitarized, 3:50
Germans hated the Versailles treaty, and Hitler’s successful challenge made him more popular at home. The Western democracies denounced his moves but took no real action. Instead, they adopted a policy of appeasement, or giving in to the demands of an aggressor in order to to keep the peace.
The World At War - Appeasement, 6:54
The Western policy of appeasement developed for a number of reasons. France was demoralized, suffering from political divisions at home. It could not take on Hitler without British support. The British, however, had no desire to confront the German dictator. Some even thought that Hitler’s actions constituted a justifiable response to the terms of the Treaty of Versailles, which they believed had been too harsh on Germany.
In both Britain and France, many saw Hitler and fascism as a defense against a worse evil—the spread of Soviet communism. Additionally, the Great Depression sapped the energies of the Western democracies. Finally, widespread pacifism, or opposition to all war, and disgust with the destruction from the previous war pushed many governments to seek peace at any price.
As war clouds gathered in Europe in the mid-1930s, the United States Congress passed a series of Neutrality Acts. One law forbade the sale of arms to any nation at war. Others outlawed loans to warring nations and prohibited Americans from traveling on ships of warring powers. The fundamental goal of American policy, however, was to avoid involvement in a European war, not to prevent such a conflict.
The Mood Of The USA 1939 to Pearl Harbor, 2:16
New Alliances
In the face of the apparent weakness of Britain, France, and the United States, Germany, Italy, and Japan formed what became known as the Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis. Known as the Axis powers, the three nations agreed to fight Soviet communism. They also agreed not to interfere with one another’s plans for territorial expansion. The agreement cleared the way for these anti-democratic, aggressor powers to take even bolder steps.
Berlin-Rome-Tokyo 1937, 2:36
In Italy, Mussolini decided to act on his own imperialist ambitions. Italy’s defeat by the Ethiopians at the battle of Adowa in 1896 still rankled. In 1935, Italy invaded Ethiopia, located in northeastern Africa. Although the Ethiopians resisted bravely, their outdated weapons were no match for Mussolini’s tanks, machine guns, poison gas, and airplanes. The Ethiopian king Haile Selassie (hy luh suh lah see) appealed to the League of Nations for help. The League voted sanctions against Italy for violating international law. But the League had no power to enforce the sanctions, and by early 1936, Italy had conquered Ethiopia.
Union with Austria
From the beginning, Nazi propaganda had found fertile ground in Austria. By 1938, Hitler was ready to engineer the Anschluss (ahn shloos), or union of Austria and Germany. Early that year, he forced the Austrian chancellor to appoint Nazis to key cabinet posts. When the Austrian leader balked at other demands in March, Hitler sent in the German army to “preserve order.” To indicate his new role as ruler of Austria, Hitler made a speech from the Hofburg Palace, the former residence of the Hapsburg emperors.
The Anschluss violated the Versailles treaty and created a brief war scare. Some Austrians favored annexation. Hitler quickly silenced any Austrians who opposed it. And since the Western democracies took no action, Hitler easily had his way.
Demands and Appeasement
Germany turned next to Czechoslovakia. At first, Hitler insisted that the three million Germans in the Sudetenland (soo day tun land)—a region of western Czechoslovakia—be given autonomy. Czechoslovakia was one of only two remaining democracies in Eastern Europe. (Finland was the other.) Still, Britain and France were not willing to go to war to save it. As British and French leaders searched for a peaceful solution, Hitler increased his demands. The Sudetenland, he said, must be annexed to Germany.
At the Munich Conference in September 1938, British and French leaders again chose appeasement. They caved in to Hitler’s demands and then persuaded the Czechs to surrender the Sudetenland without a fight. In exchange, Hitler assured Britain and France that he had no further plans to expand his territory.
After the horrors of World War I, Western democracies desperately tried to preserve peace during the 1930s while ignoring signs that the rulers of Germany, Italy, and Japan were preparing to build new empires. Despite the best efforts of Neville Chamberlain and other Western leaders, the world was headed to war again.
British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain spoke to a jubilant crowd upon returning to London from a conference with Adolf Hitler in Munich, Germany, in September 1938:
“For the second time in our history, a British Prime Minister has returned from Germany bringing peace with honor. I believe it is peace for our time . . . Go home and get a nice quiet sleep.”
"Peace in our Time," Chamberlain, September 1938, 3:24
Great Britain and France React
Hitler and the Soviets
Just as Churchill predicted, Europe plunged rapidly toward war. In March 1939, Hitler broke his promises and gobbled up the rest of Czechoslovakia. The democracies finally accepted the fact that appeasement had failed. At last thoroughly alarmed, they promised to protect Poland, most likely the next target of Hitler’s expansion.
In August 1939, Hitler stunned the world by announcing a nonaggression pact with his great enemy—Joseph Stalin, the Soviet dictator. Publicly, the Nazi-Soviet Pact bound Hitler and Stalin to peaceful relations. Secretly, the two agreed not to fight if the other went to war and to divide up Poland and other parts of Eastern Europe between them.
Stalin-Hitler pact commemorated, 3:58
The pact was based not on friendship or respect but on mutual need. Hitler feared communism as Stalin feared fascism. But Hitler wanted a free hand in Poland. Also, he did not want to fight a war with the Western democracies and the Soviet Union at the same time. For his part, Stalin had sought allies among the Western democracies against the Nazi menace. Mutual suspicions, however, kept them apart. By joining with Hitler, Stalin tried to protect the Soviet Union from the threat of war with Germany and grabbed a chance to gain land in Eastern Europe.
Reading Check
Identifying
Where did Hitler believe he could find more "living space" to expand Germany?
The Japanese Path to War
One of the earliest tests had been posed by Japan. Japanese military leaders and ultranationalists thought that Japan should have an empire equal to those of the Western powers. In pursuit of this goal, Japan seized Manchuria in 1931. When the League of Nations condemned the aggression, Japan simply withdrew from the organization. Japan’s easy success strengthened the militarist faction in Japan. In 1937, Japanese armies overran much of eastern China, starting the Second Sino-Japanese War. Once again, Western protests did not stop Japan.
Japanese Invasion of Manchuria, 2:06
When war broke out in Europe in 1939, the Japanese saw a chance to grab European possessions in Southeast Asia. The rich resources of the region, including oil, rubber, and tin, would be of immense value in fighting its war against the Chinese.
In 1940, Japan advanced into French Indochina and the Dutch East Indies. To stop Japanese aggression, the United States banned the sale of war materials, such as iron, steel, and oil to Japan. Japanese leaders saw this move as an attempt to interfere in Japan’s sphere of influence.
Asian Holocaust - Asia-Pacific theatre of war, World War II, 1:07
This short clip highlights the human scale of the tragedy in the Second World War Asia-Pacific theatre. Between 1931-1945, Japanese Imperial Forces invaded and occupied parts of China, Manchukuo, Dutch East Indies (Indonesia), New Guinea, French Indochina (Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia), British Malaya, Singapore, Burma, Borneo, American-occupied Philippines. This clip is part of a project on www.asianholocaust.org to gather resources and information to commemorate the Asian and Allied victims of this epic conflict.
Japan and the United States held talks to ease the growing tension. But extreme militarists, such as General Tojo Hideki, hoped to expand Japan’s empire, and the United States was interfering with their plans.
War with China
The New Asian Order
Reading Check
Explaining
Why did Japan want to establish a New Order in East Asia?
Ch. 19 Resources
See the war through the eyes of soldiers, secret agents, pilots and evacuees.
Life for children during the war.
Listen to an air raid warning.
The blitz and the home front in the UK.
Churchill and the bombing of Dresden
London, England during World War II
Los Lobos 'One Time, One Night' 1992
Songwriter: Bob Dylan
A wise man was telling stories to me
About the places he had been to
And the things that he had seen
A quiet voice is singing something to me
An age old song about the home of the brave
In this land here of the free
One time one night in America
A lady dressed in white with the man she loved
Standing along the side of their pickup truck
A shot rang out in the night
Just when everything seemed right
Another headline written down in America
The guy that lived next door in #305
Took the kids to the park and disappeared
About half past nine
Who will ever know
How much she loved them so
That dark night alone in America
A quiet voice is singing something to me
An age old song about the home of the brave
In this land here of the free
One time one night in America
Four small boys playing ball in a parking lot
A preacher, a teacher, and the other became a cop
A car skidded into the rain
Making the last little one a saint
One more light goes out in America
A young girl tosses a coin in the wishing well
She hopes for a heaven while for her
There's just this hell
She gave away her life
To become somebody's wife
Another wish unanswered in America
People having so much faith
Die too soon while all the rest come late
We write a song that no one sings
On a cold black stone
Where a lasting peace will finally bring
The sunlight plays upon my windowpane
I wake up to a world that's still the same
My father said to be strong
And that a good man could never do wrong
In a dream I had last night in America
A wise man was telling storie to me
About the places he had been to
And the things that he had seen
A quiet voice is singing something to me
An age old song about the home of the brave
In this land here of the free
One time one night in America
Lyrics reproduced for educational purposes only; copyright remains in the hands of the legitimate owner.
Ritchie Valens - La Bamba
Los Lobos - La Bamba
The Ch. 17 Sec. 3 Quiz is on Wednesday. Be sure to consult the Chapter 17 Section 3 Quiz Study Prep Page.
Email to gmsmith@shanahan.org
Tuesday: p. 577, Reading Check
Identifying
Which group did Mao believe would start the Communist revolution in China?
p. 578 Picturing History
p. 578
Reading Check
Explaining
Why did it seem that communism was no longer a threat to China after the Long March?
p. 579
Reading Check
Identifying
What was the intended final stage of Chiang Kai-shek's reform program?